1. Introduction:
Protein stands as a fundamental building block of nutrition, crucial for supporting various bodily functions and maintaining optimal health. Amidst the array of protein sources available, steak holds perennial favorite positions among meat enthusiasts.
Its taste, versatility in cooking, and perceived muscle-building properties make it a staple in many diets. However, as individuals strive to meet their protein needs, understanding the protein content of steak becomes paramount.
In this blog, we will explore how much protein is in a pound of steak, nutritional value tips for integrating in the meal plan.
Read More: What’s the Difference Between Ground Beef and Ground Chuck
2. Understanding the macronutrient – Protein:
Protein is a macronutrient essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of the body’s tissues. It plays a critical role in various physiological processes, including muscle development, immune function, and hormone production. Comprising amino acids, the building blocks of protein, this nutrient is an important ingredient for health.
The recommended daily intake of proteins depends on variety of factors. These include age, sex, activity level, and individual health goals. Proteins can be sourced from a variety of foods, including both animal and plant-based foods.
Animal sources products having adequate proportions of amino acid such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy are rich sources of complete protein, while plant-based sources like beans, lentils, tofu, nuts, and seeds require careful planning to ensure all essential amino acids are obtained.
In the realm of balanced nutrition, adequate protein intake serves a vital function in appetite control, weight management, and the maintenance of lean muscle mass, particularly for active individuals.
Read More: What is the Difference Between White and Dark meat? Which is Better
3. How Much Protein is in a Pound of Steak?
Understanding the protein content of steak is crucial for individuals seeking to meet their dietary protein needs. When considering how much protein is in a pound of steak, several factors come into play, including the type of steak and its lean-to-fat ratio.
On average, a pound of steak contains approximately 80-100 grams of protein. However, this can vary depending on the specific cut of meat and its fat content. Leaner cuts such as sirloin or tenderloin typically contain more protein per pound compared to fattier cuts like ribeye or T-bone.
To provide a more specific example, a pound of sirloin steak, which is relatively lean, may contain around 90-95 grams of protein. Conversely, a pound of ribeye steak, which has more marbling and higher fat content, might contain slightly less protein, around 80-85 grams.
It’s essential to consider the protein content alongside other nutrients present in steak, such as iron, zinc, and B vitamins. These nutrients contribute to overall health and well-being and complement the protein content of the meat.
Read More: How Many Pounds of Meat Per Person? What is the Right Amount?
4. Comparing the Protein Content of Steak to Other Meat Sources:
When considering protein sources in your diet, it’s essential to compare the protein content of steak with other meat options to make informed choices about your nutrition. Let’s explore common sources of meat protein content:
Chicken Breast:
Chicken breast is often touted as a lean protein option, and for good reason. It typically contains around 25 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving. However, leaner cuts of steak, such as sirloin or tenderloin, may offer similar or even higher protein content per serving.
Pork Loin:
Pork loin is another lean meat option that provides a substantial amount of protein. A 3-ounce serving of pork loin typically contains around 22 grams of protein. While slightly lower than some cuts of steak, pork loin is still a valuable protein source to consider in your diet.
Fish (Salmon):
Fish, particularly fatty varieties like salmon, is prized for its omega-3 fatty acids and protein content. A 3-ounce serving of salmon typically provides around 22 grams of protein, similar to pork loin. While fish offers additional nutritional health benefits beyond protein, such as heart-healthy fats, it’s essential to vary your protein sources for a well-rounded diet.
Ground Beef (90% lean):
Ground beef is a versatile meat option commonly used in various dishes. A 3-ounce serving of 90% lean ground beef typically contains around 21 grams of protein. While slightly lower in protein compared to some cuts of steak, ground beef can still contribute significantly to your protein intake.
Turkey Breast:
Turkey breast is another lean protein source that offers similar protein content to chicken breast. A 3-ounce serving of turkey breast typically provides around 25 grams of protein, comparable to steak and chicken breast. Incorporating turkey breast into your diet adds variety and nutritional value to your meals.
4. Nutritional Benefits of Steak:
Steak, for its savory taste and juicy texture, offers a range of nutritional benefits. As a part of a balanced diet, steak offer good sources of health and well-being. Here are some:
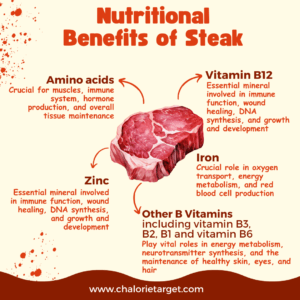
- High-Quality Protein: High-quality protein with essential amino acids is crucial for muscles, immune system, hormone production, and overall tissue maintenance.
- Iron: Steak is one of the best dietary sources of heme iron, the most readily absorbed form of iron by the body. Iron plays a crucial role in oxygen transport, energy metabolism, and red blood cell production. Adequate iron intake is particularly important for preventing iron deficiency anemia.
- Zinc: Steak is also a significant source of zinc, an essential mineral involved in immune function, wound healing, DNA synthesis, and growth and development. Zinc deficiency can impair immune function and lead to a variety of health issues.
- Vitamin B12: Steak is an excellent source of vitamin B12, a water-soluble vitamin essential for nerve function, DNA synthesis, red blood cell formation, and energy metabolism. Adequate intake of vitamin B12 is critical for maintaining neurological health and preventing megaloblastic anemia.
- Other B Vitamins: Steak contains various B vitamins, including niacin (vitamin B3), riboflavin (vitamin B2), thiamine (vitamin B1), and pyridoxine (vitamin B6). These vitamins play vital roles in energy metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, and the maintenance of healthy skin, eyes, and hair.
- Muscle Health: The amino acids and nutrients found in steak are essential for maintaining muscle mass, strength, and function, particularly in active individuals and athletes. Including steak in the diet can support muscle repair and recovery after exercise.
Read More: Why are Carbohydrates and Fats Considered High Energy Foods
5. Protein’s Contribution to Muscle Growth from a Fitness Angle:
Proteins serve as the building blocks for muscle tissue repair, growth, and maintenance. Firstly, it provides the essential amino acids the process through which new muscle tissue is formed. Consuming an adequate amount of protein post-exercise helps replenish amino acid stores and promotes muscle repair and growth.
From a fitness perspective, the timing and distribution of protein intake throughout the day also play a significant role in maximizing muscle growth and recovery. Consuming protein-rich meals or snacks in close proximity to exercise sessions can enhance muscle protein synthesis and promote faster recovery from intense workouts.
Furthermore, the quality of protein sources consumed is a critical consideration for individuals pursuing fitness goals. High-quality protein sources, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, and plant-based sources like tofu and legumes, provide ample amounts of essential amino acids needed for muscle repair and growth.
By understanding the intricate relationship between protein intake, muscle growth, and exercise, fitness enthusiasts can optimize their nutritional strategies to support their physical performance and overall fitness journey.
6. The Role of Steak in Weight Loss and Health:
The role of steak in weight loss and health is multifaceted, encompassing its high protein content, nutrient density, and practical considerations. With its renowned protein content, steak serves as a valuable component of weight loss diets by promoting satiety, reducing appetite, and preserving lean muscle mass during calorie restriction.
Additionally, steak is rich in essential nutrients such as iron, zinc, and vitamin B12, supporting metabolic function and overall vitality. However, portion control and mindful selection of lean cuts are crucial to mitigate calorie intake while reaping the benefits of steak’s protein content and satiating properties.
By balancing steak consumption with other macronutrients and considering individual health factors, individuals can incorporate steak into a balanced diet to support their weight loss goals and enhance overall health.
Final Thoughts:
In conclusion, when considering the query “How Much Protein is in a Pound of Steak,” it’s clear that steak offers a significant protein punch alongside a plethora of other nutrients. Understanding its protein content underscores its value in weight management and overall health.
By being mindful of portion sizes and selecting lean cuts, individuals can harness the protein-rich benefits of steak to support their dietary goals.
this knowledge, incorporating steak into a balanced diet becomes not only a flavorful choice but also a strategic one for optimizing protein intake and promoting overall well-being.
